Researcher: Pier Rubesa (Ir. of sound), Grandson, Switzerland
Bioscope studies ordered by SA Dynamized Technologies on 23.07.2025 & 13.09.2016.
Process: The Bioscope is a spectrometer which analyses changes in the electrical properties of water following the emission of a low frequency electrical signal (113 Hz) sent into the water via an electrode. The interpretation of the measurements (distortion between transmitted & received signal) is computer assisted. The analysis mainly focuses on energy displacements (in terms of electrons / protons), electrical field dynamics, in particular towards the low frequency ranges = frequencies emitted by the “living” * = notably the cells
The Bioscope observes a shift in energy towards specific frequency ranges, which indicates a more organized, structured and coherent electrodynamic organization in biodynamized water
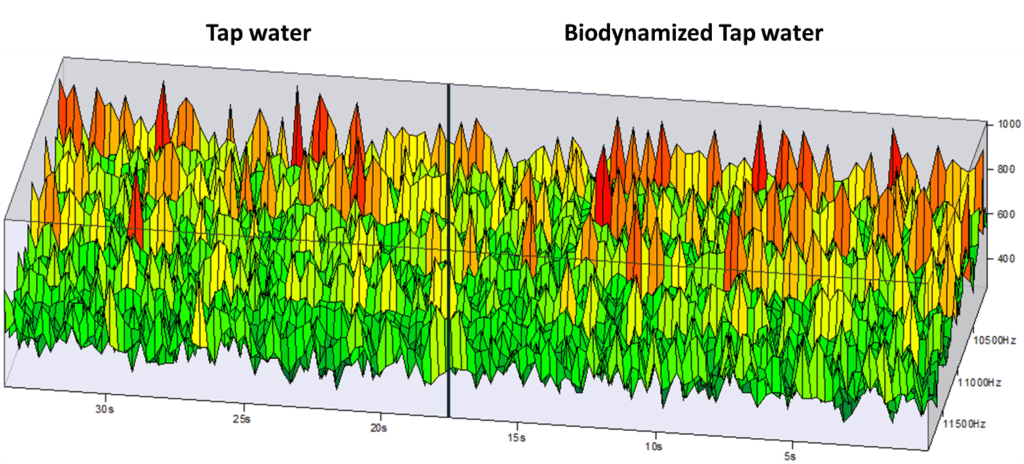
Surface spectrum before & after the passage of water in the Biodynamizer: we observe ashift in energy intensity toward specific frequency bands (this is manifested by the displacement of the amplitude peaks, graph 1)
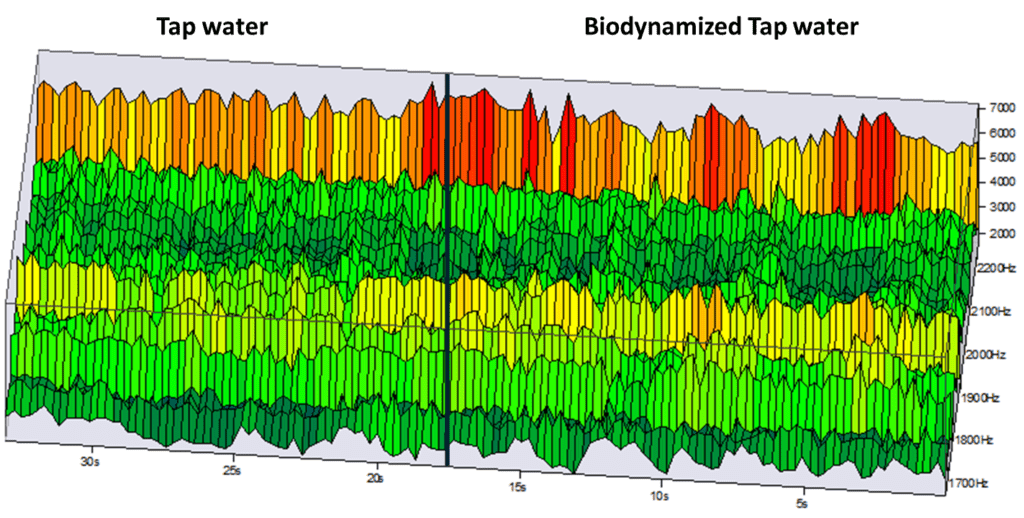
Surface spectrum before & after the passage of water in the Biodynamizer: we notice a pulse of energy at regular (periodic) and systematic rhythms, which demonstrates a more structured and coherent electrodynamic organization of the biodynamized water (graph 2)
The Bioscope is a spectrometer that measures the electrodynamic characteristics of water after emitting acoustic signals (its dielectric permittivity, or the organization of electrical charges). It observed a shift in energy (that of the low-frequency excitation signal of 113 Hz sent by an electrode in the biodynamized water) toward specific frequency bands (Hz) whose amplitudes (eV), positive and negative, change by up to 6 dB (i.e., the intensity and quantity of light reflected per wavelength). For the biodynamized water, these amplitude changes (in electron volts) occur toward certain harmonic (interrelated) frequencies (in Hertz), at regular (periodic) and systematic rythms, which demonstrates a more organized, structured and coherent electrodynamic organization of biodynamized water (= a modification of the spectral profile of dynamized water manifested by changes in amplitudes or intensities of energy at certain acoustic frequencies).
This observation can be explained by the restructuring of the hydrogen bonds in the clusters of water molecules induced by its dynamization (because water cluster reorganization modifies vibrational, rotational, and collective signal excitations, any re-patterning of molecular structure could modulate how water absorbs/transmits/reflects sound or electromagnetic energy—manifesting as amplitude changes at specific frequencies).
This energy reallocation modifies the physicochemical and biological properties of biodynamized water!

Pier Rubesa + Bioscope
* William Ross Adey professor of anatomy and physiology at the University of California “Electromagnetic Fields and the Essence of Living Systems »:“Laboratory studies have tested a spectrum of EM fields for bioeffects at cell and molecular levels, focusing on exposures at athermal levels. A clear emergent conclusion is that many observed interactions are not based on tissue heating. Modulation of cell surface chemical events by weak EM fields indicates a major amplification of initial weak triggers associated with binding of hormones, antibodies, and neurotransmitters to their specific binding sites. Calcium ions play a key role in this amplification. These studies support new concepts of communication between cells across the barriers of cell membranes; and point with increasing certainty to an essential physical organization in living matter, at a far finer level than the structural and functional image defined in the chemistry of molecules.There is increasing evidence that these events relate to quantum states and resonant responses in biomolecular systems, and not to equilibrium thermodynamics associated with thermal energy exchanges and tissue heating.”





