The dynamization process using the Biodynamizer brings light, and therefore energy, into the water and into living organisms!
Analyses published on November 26, 2025 and December 30, 2025 by a peer-review committee, the Editorial Board of the South Florida Journal of Development, University of South Florida, USA

Biophotonic analysis of biodynamized water
Researcher: Mr. Olivier Salières, Electronics Engineer (ENSICA). Analysis performed by the ENERLAB laboratory in Nice, France on November 4, 2025, reviewed by a scientific peer review committee from the University of South Florida, article published by the South Florida Journal of Development in November 2025.
Measuring Instruments:
A high-sensitivity Berthold Lumat LB 9508 luminometer (detecting light intensities below 10⁻¹⁶ W/cm²!) measures light intensity (bioluminescence reactions) in the 380-630 nm spectral range (visible light). A photomultiplier tube (PMT) is used to amplify the light (the Luminometer is capable of detecting the light of a candle from 300 km away!). Light can be quantified, and its intensity expressed as the number of photons converted to RLU (Relative Light Units = Biophotons), i.e., the number of photons emitted per second per cm². The luminometer is controlled by ICE software. 11 independent measurements were performed for each sample to ensure statistically significant reproducibility.
Additional measurements of biophotons emitting in the 435-500 nm spectral band (using a Schott BG-7 filter) to target the blue-green range which has an effect on the mitochondria.


Results of the biophotonic analysis of biodynamized water
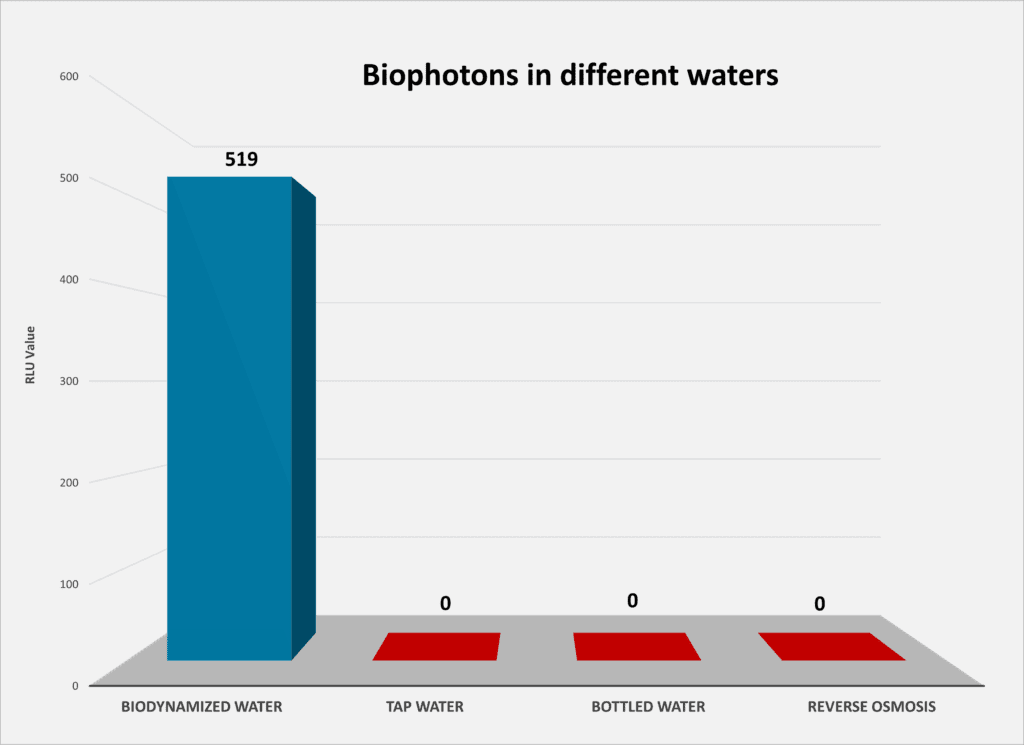
1) Biodynamized tap water emits a lot of bioluminescence in the form of biophotons (519 RLU/second/cm2) which is absolutely not the case for other waters measured (0 RLU for tap water, bottled mineral water, reverse osmosis water) ; See also in this regard our AEP (Electrophotonic Analysis) and the electrophotonic expertise by Prof. M. Henry
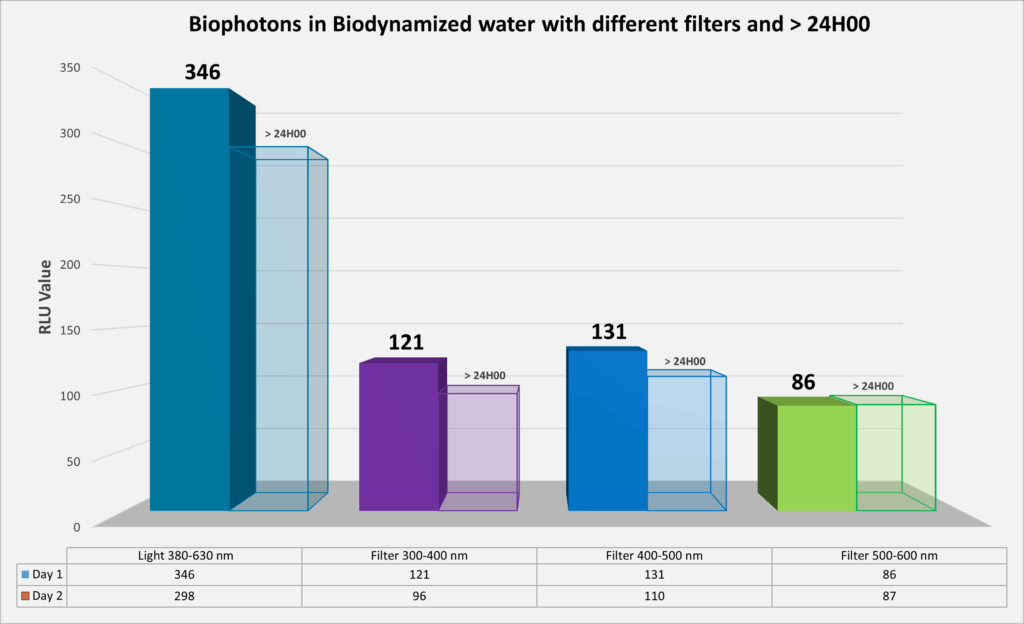
2) Decomposition of light in biodynamized water and persistence over time (> 24H00) :
- 380-630 nm: 100% > 24H00: 86% (-14%: 346 RLU -> 298 RLU)
- 300-400 nm: 35% > 24H00: 79% (-21%: 121 RLU -> 96 RLU)
- 400-500 nm: 38% > 24H00: 84% (-16%: 131 RLU -> 110 RLU)
- 500-600nm: 25% > 24H00: 100% (-0%: 86 RLU -> 87 RLU)
See in this regard the shifts in energy amplitude towards specific frequency ranges in spectrometry (Bioscope) and the duration of red blood cell unstacking
3) Metabolic functions of light present in biodynamized water, induced in metabolism by the stimulation of this light on the body’s biochemical signaling processes. These functions depend on the different wavelengths of light that have been decomposed by the filters:
- 300-400 nm (violet-blue): mitochondrial function (these are the energetic power plants of our cells) & tissue repair processes
- 400-500 nm (blue-cyan): redox & mitochondrial homeostasis
- 500-600 nm (green-yellow-orange): coherent photonic stimulation of cellular metabolism
It should be noted that 98% of the light decomposed by the filters was successfully recomposed, which proves the relevance of the protocol and validates the consistency of the measurements obtained.
Regarding redox potential, see bioelectronic analysis

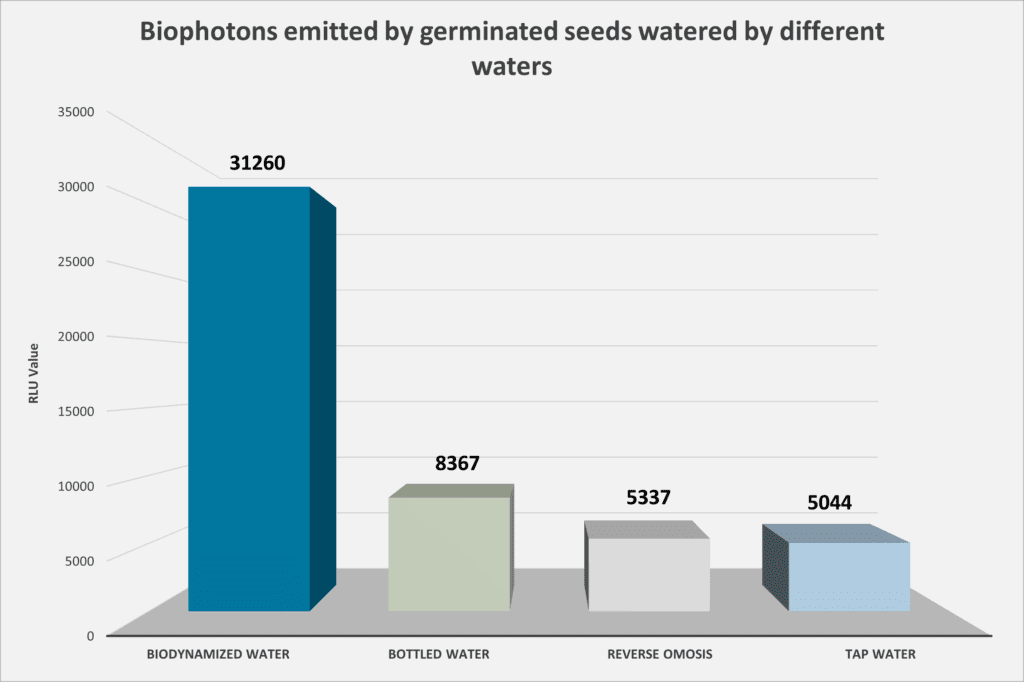
Results of the biophotonic analysis of germinated seeds
4) There is a correlation between the energy level (biophotons) observed in biodynamized water and that observed in germinated seeds: germinated seeds watered with biodynamized water emit six times more biophotons (31,260 RLU/second/cm²) than those watered with other measured waters. These emit between 73% and 84% fewer biophotons! This demonstrates that the energetic quality of the biodynamized water is transferred to the living organism. It also suggests that the biophotonic radiation from the seed’s own biochemical activity is complemented and amplified by the biophotonic emission of biodynamized water. This allows for a higher level of functional vitality in the plant’s biological processes.
See also, in this regard, our observation on sprouted seeds
Biophotons are signals in the form of light particles that originate spontaneously from either a biological organism or the environment such as the sun (in which case they are then captured by Biodynamized water). They are carriers of structured and coherent energy (coded information -> synchronized oscillations), emitted at ultra-low frequencies (UPE), that of the visible light spectrum. They activate and coordinate the billions of chemical reactions that occur every second in our cells (cell communication). They contain and transport a significant amount of energy per photon (eV) due to their higher frequencies and shorter wavelengths. These high-energy photons can interact with cellular photoactive systems and contribute to stimulating ATP production by mitochondria (i.e., cellular energy), the redox potential, …
The intensity of biophotons is extremely low, 1000 times lower than the sensitivity of the human eye! 1500 scientific publications have been produced in peer-reviewed journals concerning the functions of biophotons.
In this context, biodynamized water can be considered an interface that better captures and contains more photonic energy. It therefore possesses an enhanced capacity to transmit this coherent and harmonious biological energy, which is beneficial to living organisms.
As it passes through the water, biophotonic energy restructures its molecules (via its hydrogen bonds) and informs it (the water captures, stores, and transmits this information by oscillating synchronously in phases of coherence).
These biophotons thus represent an index of the water’s energetic and biological quality. They do not reflect biochemical activity, but rather a quantity and a state of electrodynamic organization that allows for improved energy transfer and coherent information conducive to life (energy vitality).
Origin of biophotons: mitochondria, DNA and Biodynamized water !
Biophotons are particles of light that originate from:
1) biological organisms: biophotons are biological light signals emitted spontaneously by biological organisms (plant, animal, or human), reflecting their cellular vitality and overall health. Their source of emission is found in:
a. Mitochondria (organelles responsible for converting metabolic energy)
b. DNA (a molecule present in the chromosomes of our cell nuclei), which acts as a kind of electromagnetic antenna, capturing energy from the environment and then re-emitting it after encoding it coherently and in a structured way (by the nucleotide sequences of DNA (A, T, G, C)), through biophotons in the organism. Biophotons are therefore vectors of biological electromagnetic energy between the cells of the human body.
2) Biodynamized Water: Biophotons are light signals originating from the energy of our immediate environment (sunlight, UV, IR, scalar, etc.) which the biodynamization of water allows it to better capture, stock, and inform.
Biodynamization generates kinetic and magnetic energy in the water while transmitting mineral frequencies and photonic resonances, which, along with the energy of the environment, will “restructure” and “activate” it.
a.“Restructuring” from the perspective of its hydrogen bonds due to water’s dipolar properties. This molecular restructuring of water, through polarization (permanent magnets) and vortices, should allow the energy flowing through it to oscillate synchronously within quantum coherence domains and thus transmit frequencies, which can be described as information, to the cells.
b.“Activating,” from an energetic perspective, means the excitation of its electrons, which, by absorbing energy from biodynamization and/or the environment, would move to a higher-energy orbit (further from the nucleus).